SL 151
Bremmer
October 12, 1999
2nd Exam - - Chapters 13-15
Part I. Multiple Choice (3 points each). Indicate the best
answer for each question.
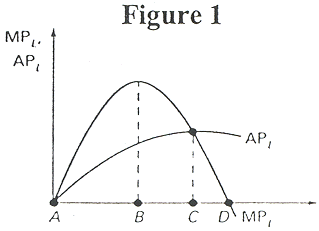
- Referring to Figure 1, diminishing marginal returns sets in at:
- labor level A.
- labor level B.
- labor level C.
- labor level D.
- According to Figure 1, output is maximized at:
- labor level A.
- labor level B.
- labor level C.
- labor level D.
- In Figure 1, a profit-maximizing firm will never hire labor beyond:
- labor level A.
- labor level B.
- labor level C.
- labor level D.
- In Figure 1, average variable cost will be ____ if the firm hires
labor at point ___ .
- maximized; B
- minimized; B
- maximized; C
- minimized; C
- If you know that with 8 units of output, average fixed cost is
$12.50 and average variable cost is $81.25, then total cost at this output
level is:
- $93.75.
- $97.78.
- $750.
- $880.
- If marginal cost is greater than average variable cost for a given
level of output, then:
- average total cost must be increasing.
- average fixed cost must be increasing.
- average variable cost must be increasing.
- Both A and C.
- None of the above.
- Because the marginal product of a variable input at first increases
and then decreases as the output of the firm is increased:
- average fixed cost will rise beyond the point of diminishing
returns.
- average total cost at first increases and then decreases.
- variable cost at first increases at an increasing rate and
then increases at a decreasing rate.
- total cost at first increases at a decreasing rate and then
increases at an increasing rate.
- Other things being equal, if the wage rates paid to a firm's labor
inputs were to fall, we would expect:
- the ATC, AFC, and MC curves to fall.
- the ATC and AFC curves to fall.
- the ATC, AVC, AFC, and MC curves to fall.
- the ATC, AVC, and MC curves to fall.
- Which of the following would contribute most to a firm experiencing
"economies of scale"?
- Rising long-run average cost.
- Deterioration of information and control within a firm.
- The law of diminishing marginal returns.
- Increased specialization of production within a firm.
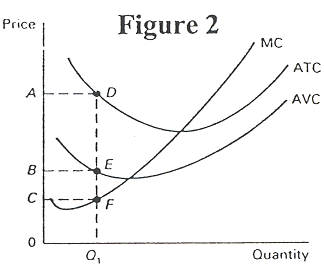
- Given Figure 2, which of the following statements is true?
- At output level Q1, the marginal product of labor
is increasing.
- At Q1, total cost is equal to area 0BEQ1.
- If the firm shuts down in the short run, it will lose area
BADE.
- If the firm shuts down in the short run, its loss equals
line segment DE.
- All of the above except D.
- A purely competitive firm's output is currently such that its
marginal cost is $4 and marginal revenue is $5. Assuming profit maximization,
the firm should:
- cut its price and raise its output.
- raise its price and cut output.
- leave price unchanged and raise output.
- leave price unchanged and cut output.
- If the input prices increase when new firms enter a perfectly
competitive market:
- the long-run industry supply must be downward sloping.
- the long-run industry supply curve must be perfectly elastic.
- the long-run industry supply curve must be upward sloping.
- the long-run industry supply curve is that portion of the
MC curve above the AVC curve.
- If a purely competitive industry is in long-run equilibrium and
property taxes (a fixed cost) decrease, which of the following will happen
in the short run?
- Market price will decrease, market output will increase,
the output of the typical firm will decrease, and firms earn economic profits.
- Market price will increase, market output will decrease,
the output of the typical firm will increase, and firms incur losses.
- Market price, market output, and the output of the typical
firm remains unchanged; but, firms earn economic profits.
- Market price, market output, and the output of the typical
firm remains unchanged; but, firms incur losses.
- If a purely competitive industry is in long-run equilibrium and
property taxes (a fixed cost) decrease, which of the following will happen
in the long run?
- Firms exit the industry, market price will increase, market
quantity will decrease, the output of the typical firm will increase, and
the firms in the industry earn only normal profits.
- Firms enter the industry, market price will decrease, market
quantity will increase, the output of the typical firm will decrease, and
the firms in the industry earn only normal profits.
- The firms will continue to incur losses in the long run.
- The firms will continue to earn economic profits in the long
run.
- Which of the following statements is true?
- A monopolist faces a perfectly elastic demand curve.
- For a monopolist, MR = P.
- If demand is elastic, a monopolist's MR is negative.
- All of the above.
- None of the above.
Part II. Short Answer Questions (55 points). Give a concise,
but complete answer for each of the following questions. When appropriate,
use math, graphs, or equations to help explain your answer.
- Why would a firm be interested in knowing its long-run average
cost curve? Using a graph, explain in words and illustrate how the long-run
average cost curve is derived. Using your graph, identify:
- the optimal size of the firm,
- a plant size that the firm would use undercapacity,
- a plant size that the firm would use over capacity,
- when the firm experiences economies of scale, and
- when the firm experiences diseconomies of scale. (10 points).
- Compare and contrast the assumptions of the perfectly competitive
model and the pure monopoly model. (10 points)
- Illustrate graphically and explain why a competitive firm would
shut down in the short run if P < AVC. (10 points)
- Fill in the missing blanks of the following table. (10 points)
| Q |
AFC |
VC |
TC |
ATC |
MC |
| 10 |
10 |
|
|
|
10 |
| 20 |
|
180 |
|
|
|
| 30 |
|
|
|
|
|
| 40 |
|
|
430 |
|
9 |
| 50 |
|
|
|
10.80 |
|
- Assume a perfectly competitive, decreasing-cost industry is in
long-run equilibrium. Using two graphs - - one showing the market demand
and supply curves, and the other showing the average cost curves of the
typical firm - - explain what happens in the short run and in the long
run if demand decreases. (10 points)
6. Does the following short-run production function exhibit the law
of diminishing marginal returns? Explain. (5 points)
| Q |
0 |
5 |
20 |
32 |
42 |
50 |
55 |
58 |
58 |
56 |
| L |
0 |
1 |
2 |
3 |
4 |
5 |
6 |
7 |
8 |
9 |

