CSSE 290 Web Programming
Lecture 21: XML and JSON
Reading: 12.3, 12.4
Attribution:Except where otherwise noted, the contents of this document are Copyright 2012 Marty Stepp, Jessica Miller, and Victoria Kirst. All rights reserved. Any redistribution, reproduction, transmission, or storage of part or all of the contents in any form is prohibited without the author's expressed written permission.
Otherwise noted: Claude Anderson was given permission to modify the slides for CSSE 290 at Rose-Hulman by author Jessica Miller.
The authors' original slides, based on Web Programming Step by Step, can be seen at http://webstepbook.com.
Some of the examples in some days' slides are from David Fisher at Rose-Hulman, who was kind enough to allow me to use them.
My intention is to mark these examples with [DSF].
Storing structured data in arbitrary text formats (bad)
My note: BEGIN FROM: Alice Smith (alice@example.com) TO: Robert Jones (roberto@example.com) SUBJECT: Tomorrow's "Birthday Bash" event! MESSAGE (english): Hey Bob, Don't forget to call me this weekend! PRIVATE: true END
- Many apps make up their own custom text format for storing structured data.
- We could also send a file like this from the server to browser with Ajax.
- What's wrong with this approach?
XML: A better way of storing data
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?> <note private="true"> <from>Alice Smith (alice@example.com)</from> <to>Robert Jones (roberto@example.com)</to> <subject>Tomorrow's "Birthday Bash" event!</subject> <message language="english"> Hey Bob, Don't forget to call me this weekend! </message> </note>
- eXtensible Markup Language (XML) is a format for storing nested data with tags and attributes
- A lot like HTML, but you can make up any tags and attributes you want
- Lots of existing data on the web is stored in XML format
What is XML?
- XML is a "skeleton" for creating markup languages
- you decide on an XML "language" of tags and attributes that you want to allow in your app
- XML syntax is mostly identical to HTML's:
<element attribute="value">content</element> - the HTML/XML tag syntax is a nice general syntax for describing hierarchical (nested) data
- when you choose to store data in XML format (or access external XML data), you must decide:
- names of tags in HTML:
h1,div,img, etc. - names of attributes in HTML:
id/class,src,href, etc. - rules about how they go together in HTML: inline vs. block-level elements
- names of tags in HTML:
- XML presents complex data in a human-readable, "self-describing" form
Anatomy of an XML file
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?> <!-- XML prolog --> <note private="true"> <!-- root element --> <from>Alice Smith (alice@example.com)</from> <to>Robert Jones (roberto@example.com)</to> <subject>Tomorrow's "Birthday Bash" event!</subject> <message language="english"> Hey Bob, Don't forget to call me this weekend! </message> </note>
- begins with an
<?xml ... ?>header tag (prolog) - has a single root element (in this case,
note) - tag, attribute, and comment syntax is just like HTML
Uses of XML
- XML data comes from many sources on the web:
- web servers store data as XML files
- databases sometimes return query results as XML
- web services use XML to communicate
- XML is the de facto universal format for exchange of data
- XML languages are used for music, math, vector graphics
- popular use: RSS for news feeds & podcasts
What tags are legal in XML?
<measure number="1"> <attributes> <divisions>1</divisions> <key><fifths>0</fifths></key> <time><beats>4</beats></time> <clef> <sign>G</sign><line>2</line> </clef> </attributes> <note> <pitch> <step>C</step> <octave>4</octave> </pitch> <duration>4</duration> <type>whole</type> </note> </measure>
- any tags you want! examples:
- a library might use tags
book,title,author - a song might use tags
key,pitch,note
- a library might use tags
- when designing XML data, you choose how to best represent the data
- large or complex pieces of data become tags
- smaller details and metadata with simple types (integer, string, boolean) become attributes
XML and Ajax

- web browsers can display XML files, but often you instead want to fetch one and analyze its data
-
the XML data is fetched, processed, and displayed using Ajax
- (XML is the "X" in "Ajax")
- It would be very clunky to examine a complex XML structure as just a giant string!
- luckily, the browser can break apart (parse) XML data into a set of objects
- there is an XML DOM, similar to the HTML DOM
Fetching XML using Ajax (template)
new Ajax.Request("url", {
method: "get",
onSuccess: functionName
});
...
function functionName(ajax) {
do something with ajax.responseXML;
}
ajax.responseTextcontains the data in plain textajax.responseXMLis a parsed XML DOM tree object
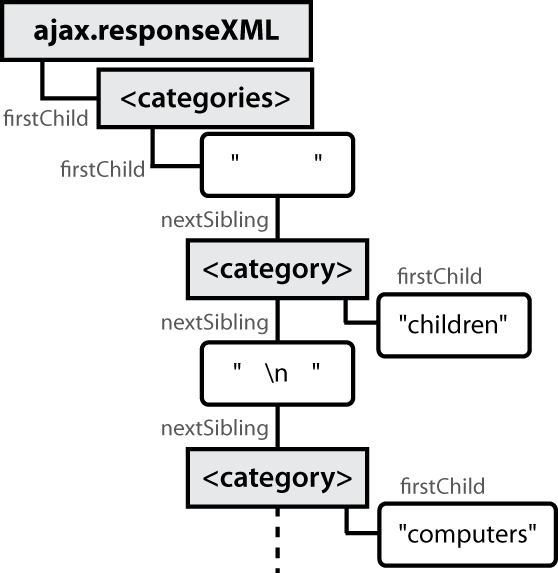
XML DOM tree structure

<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?> <categories> <category>children</category> <category>computers</category> ... </categories>
- the XML tags have a tree structure
- DOM nodes have parents, children, and siblings
- each DOM node object has properties/methods for accessing nearby nodes
Interacting with XML DOM nodes

To get a list of all nodes that use a given element:
var elms = node.getElementsByTagName("tag");
To get the text inside of a node:
var text = node.firstChild.nodeValue;
To get an attribute's value from a node:
var attrValue = node.getAttribute("name");
Differences from HTML DOM
Can't get a list of nodes by id or class using $ or $$:
var elms =$$("#main li");$("id");
Can't get/set the text inside of a node using innerHTML:
var text =$("foo").innerHTML;
Can't get an attribute's value using .attributeName:
var imageUrl =$("myimage").src;
Full list of XML DOM properties
- properties:
nodeName,nodeType,nodeValue,attributesfirstChild,lastChild,childNodes,nextSibling,previousSibling,parentNode
- methods:
getElementsByTagName,getAttribute,hasAttribute[s],hasChildNodesappendChild,insertBefore,removeChild,replaceChild
- can't use Prototype methods such as
up,down,ancestors,childElements, orsiblings
Ajax XML DOM example
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?> <employees> <lawyer money="99999.00" /> <janitor name="Ed"> <vacuum model="Hoover" /> </janitor> <janitor name="Bill">no vacuum, too poor</janitor> </employees>
// how much money does the lawyer make? var lawyer = ajax.responseXML.getElementsByTagName("lawyer")[0]; var salary = lawyer.getAttribute("money"); // "99999.00" // array of 2 janitors var janitors = ajax.responseXML.getElementsByTagName("janitor"); var vacModel = janitors[0].getElementsByTagName("vacuum")[0].getAttribute("model"); // "Hoover" var excuse = janitors[1].firstChild.nodeValue; // "no vacuum, too poor"
- How would we find out the first janitor's name?
- How would we find out how many janitors there are?
- How would we find out how many janitors have vs. don't have vacuums?
Larger XML file example
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?> <bookstore> <book category="cooking"> <title lang="en">Everyday Italian</title> <author>Giada De Laurentiis</author> <year>2005</year><price>30.00</price> </book> <book category="computers"> <title lang="en">XQuery Kick Start</title> <author>James McGovern</author> <year>2003</year><price>49.99</price> </book> <book category="children"> <title lang="en">Harry Potter</title> <author>J K. Rowling</author> <year>2005</year><price>29.99</price> </book> <book category="computers"> <title lang="en">Learning XML</title> <author>Erik T. Ray</author> <year>2003</year><price>39.95</price> </book> </bookstore>
Let's write some code for this example
Textbook example: Animal game
- Write a program that guesses which animal the user is thinking of. The program will arrive at a guess based on the user's responses to yes or no questions. The questions come from a web app named
animalgame.php. - details are in Section 12.5

Animal game (cont'd)
- The data comes in the following format:
<node nodeid="id"> <question>question text</question> <yes nodeid="id" /> <no nodeid="id" /> </node>
<node nodeid="id"> <answer>answer text</answer> </node>
- to get a node with a given id:
animalgame.php?nodeid=id - start by requesting the node with
nodeidof1to get the first question
Attacking the problem
Questions we should ask ourselves:
- How do I retrieve data from the web app? (what URL, etc.)
- Once I retrieve a piece of data, what should I do with it?
- When the user clicks "Yes", what should I do?
- When the user clicks "No", what should I do?
- How do I know when the game is over? What should I do in this case?
Debugging responseXML in Firebug
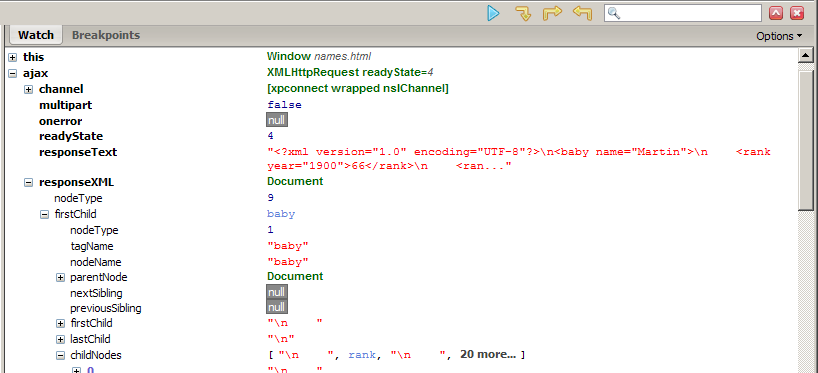
- can examine the entire XML document, its node/tree structure
Schemas and Doctypes
- "rule books" describing which tags/attributes you want to allow in your data
- used to validate XML files to make sure they follow the rules of that "flavor"
- the W3C HTML validator uses an HTML schema to validate your HTML (related to
<!DOCTYPE html>tag)
- the W3C HTML validator uses an HTML schema to validate your HTML (related to
- these are optional; if you don't have one, there are no rules beyond having well-formed XML syntax
- for more info:
- W3C XML Schema
- Document Type Definition (DTD) ("doctype")
Pros and cons of XML
- pro:
- standard open format; don't have to "reinvent the wheel" for storing new types of data
- can represent almost any general kind of data (record, list, tree)
- easy to read (for humans and computers)
- lots of tools exist for working with XML in many languages
-
con:
- bulky syntax/structure makes files large; can decrease performance (example)
- can be hard to "shoehorn" data into a good XML format
- JavaScript code to navigate the XML DOM is bulky and generally not fun
JavaScript Object Notation (JSON)


JavaScript Object Notation (JSON): Data format that represents data as a set of JavaScript objects
- invented by JS guru Douglas Crockford of Yahoo!
- natively supported by all modern browsers (and libraries to support it in old ones)
- not yet as popular as XML, but steadily rising due to its simplicity and ease of use
Recall: JavaScript object syntax
var person = {
name: "Philip J. Fry", // string
age: 23, // number
"weight": 172.5, // number
friends: ["Farnsworth", "Hermes", "Zoidberg"], // array
getBeloved: function() { return this.name + " loves Leela"; }
};
alert(person.age); // 23
alert(person["weight"]); // 172.5
alert(person.friends[2])); // Zoidberg
alert(person.getBeloved()); // Philip J. Fry loves Leela
- in JavaScript, you can create a new object without creating a class
- the object can have methods (function properties) that refer to itself as
this - can refer to the fields with
.fieldNameor["fieldName"]syntax - field names can optionally be put in quotes (e.g.
weightabove)
An example of XML data
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?> <note private="true"> <from>Alice Smith (alice@example.com)</from> <to>Robert Jones (roberto@example.com)</to> <to>Charles Dodd (cdodd@example.com)</to> <subject>Tomorrow's "Birthday Bash" event!</subject> <message language="english"> Hey guys, don't forget to call me this weekend! </message> </note>
The equivalant JSON data
{
"private": "true",
"from": "Alice Smith (alice@example.com)",
"to": [
"Robert Jones (roberto@example.com)",
"Charles Dodd (cdodd@example.com)"
],
"subject": "Tomorrow's \"Birthday Bash\" event!",
"message": {
"language": "english",
"text": "Hey guys, don't forget to call me this weekend!"
}
}
Browser JSON methods
| method | description |
|---|---|
JSON.parse(string)
|
converts the given string of JSON data into an equivalent JavaScript object and returns it |
JSON.stringify(object)
|
converts the given object into a string of JSON data (the opposite of JSON.parse)
|
- you can use Ajax to fetch data that is in JSON format
- then call
JSON.parseon it to convert it into an object - then interact with that object as you would with any other JavaScript object
JSON expressions exercise
var data = JSON.parse(ajax.responseText);
{
"window": {
"title": "Sample Widget",
"width": 500,
"height": 500
},
"image": {
"src": "images/logo.png",
"coords": [250, 150, 350, 400],
"alignment": "center"
},
"messages": [
{"text": "Save", "offset": [10, 30]}
{"text": "Help", "offset": [ 0, 50]},
{"text": "Quit", "offset": [30, 10]},
],
"debug": "true"
}
Given the JSON data at right, what expressions would produce:
- The window's title?
- The image's third coordinate?
- The number of messages?
- The y-offset of the last message?
var title = data.window.title; var coord = data.image.coords[2]; var len = data.messages.length; var y = data.messages[len - 1].offset[1];
JSON example: Books
Suppose we have a service books_json.php about library books.
-
If no query parameters are passed, it outputs a list of book categories:
{ "categories": ["computers", "cooking", "finance", ...] } -
Supply a
categoryquery parameter to see all books in one category:
http://webster.cs.washington.edu/books_json.php?category=cooking{ "books": [ {"category": "cooking", "year": 2009, "price": 22.00, "title": "Breakfast for Dinner", "author": "Amanda Camp"}, {"category": "cooking", "year": 2010, "price": 75.00, "title": "21 Burgers for the 21st Century", "author": "Stuart Reges"}, ... ] }
JSON exercise
Write a page that processes this JSON book data.
- Initially the page lets the user choose a category, created from the JSON data.
-
After choosing a category, the list of books in it appears:
Books in category "Cooking":
- Breakfast for Dinner, by Amanda Camp (2009)
- 21 Burgers for the 21st Century, by Stuart Reges (2010)
- The Four Food Groups of Chocolate, by Victoria Kirst (2005)
Working with JSON book data
function showBooks(ajax) {
// add all books from the JSON data to the page's bulleted list
var data = JSON.parse(ajax.responseText);
for (var i = 0; i < data.books.length; i++) {
var li = document.createElement("li");
li.innerHTML = data.books[i].title + ", by " +
data.books[i].author + " (" + data.books[i].year + ")";
$("books").appendChild(li);
}
}
Bad style: the eval function
// var data = JSON.parse(ajax.responseText); var data = eval(ajax.responseText); // don't do this! ...
- JavaScript includes an
evalkeyword that takes a string and runs it as code - this is essentially the same as what
JSON.parsedoes, - but
JSON.parsefilters out potentially dangerous code;evaldoesn't evalis evil and should not be used!
HW6 Preview
- Baby names>
- View it
- The php program
- Viewing results of queries

