CSSE 290 Web Programming
Lecture 19: Scriptaculous (brief look); Events
Reading: 10.2; 11.1
Attribution:Except where otherwise noted, the contents of this document are Copyright 2012 Marty Stepp, Jessica Miller, and Victoria Kirst. All rights reserved. Any redistribution, reproduction, transmission, or storage of part or all of the contents in any form is prohibited without the author's expressed written permission.
Otherwise noted: Claude Anderson was given permission to modify the slides for CSSE 290 at Rose-Hulman by author Jessica Miller.
The authors' original slides, based on Web Programming Step by Step, can be seen at http://webstepbook.com.
Some of the examples in some days' slides are from David Fisher at Rose-Hulman, who was kind enough to allow me to use them.
My intention is to mark these examples with [DSF].
10.2: Scriptaculous
- 10.1: Prototype
- 10.2: Scriptaculous
Scriptaculous overview
Scriptaculous : a JavaScript library, built on top of Prototype, that adds:
- visual effects (animation, fade in/out, highlighting)
- drag and drop
- Ajax features:
- Auto-completing text fields (drop-down list of matching choices)
- In-place editors (clickable text that you can edit and send to server)
- some DOM enhancements
- other stuff (unit testing, etc.)
Downloading and using Scriptaculous
<script src="http://ajax.googleapis.com/ajax/libs/prototype/1.7.0.0/prototype.js" type="text/javascript"></script> <script src="http://ajax.googleapis.com/ajax/libs/scriptaculous/1.9.0/scriptaculous.js" type="text/javascript"></script>
- or download it, extract its
.jsfiles to your project folder - documentation available on the Scriptaculous wiki
- Scriptaculous Effects Cheat Sheet
Visual effects
(appearing)
(disappearing)
(Getting attention)
 Click effects above
Click effects above
Adding effects to an element
element.effectName(); // for most effects // some effects must be run the following way: new Effect.name(element or id);
$("sidebar").shake();
var buttons = $$("results > button");
for (var i = 0; i < buttons.length; i++) {
buttons[i].fade();
}
- the effect will begin to animate on screen (asynchronously) the moment you call it
- six core effects are used to implement all effects on the previous slides:
Effect options
element.effectName(
{
option: value,
option: value,
...
}
);
$("my_element").pulsate({
duration: 2.0,
pulses: 2
});
- many effects can be customized by passing additional options (note the
{}) - options (wiki):
delay,direction,duration,fps,from,queue,sync,to,transition
Effect events
$("my_element").fade({
duration: 3.0,
afterFinish: displayMessage
});
function displayMessage(effect) {
alert(effect.element + " is done fading now!");
}
- all effects have the following events that you can handle:
-
beforeStart,beforeUpdate,afterUpdate,afterFinish
-
- the
afterFinishevent fires once the effect is done animating- useful do something to the element (style, remove, etc.) when effect is done
- each of these events receives the
Effectobject as its parameter- its properties:
element,options,currentFrame,startOn,finishOn - some effects (e.g.
Shrink) are technically "parallel effects", so to access the modified element, you writeeffect.effects[0].elementrather than justeffect.element
- its properties:
Learn more about Scriptaculous
- The rest of the Scriptacuous slides give a quick overview of the kinds of things that are available
- In case you are interested (optional for CSSE 290)
- Read the slides to see what is available
- More details in Section 10.2 of the textbook
- And in the Scriptaculous documentation
Drag and drop
Scriptaculous provides several objects for supporting drag-and-drop functionality:
Draggable: an element that can be draggedDraggables: manages allDraggableobjects on the pageDroppables: elements on which aDraggablecan be droppedSortable: a list of items that can be reordered
Draggable
new Draggable(element or id,
{ options }
);
- specifies an element as being able to be dragged
- options:
handle,revert,snap,zindex,constraint,ghosting,starteffect,reverteffect,endeffect - event options:
onStart,onDrag,onEnd- each handler function accepts two parameters: the
Draggableobject, and the mouse event
- each handler function accepts two parameters: the
Draggable example
<div id="draggabledemo1">Draggable demo. Default options.</div>
<div id="draggabledemo2">Draggable demo.
{snap: [40,40], revert: true}</div>
document.observe("dom:loaded", function() {
new Draggable("draggabledemo1");
new Draggable("draggabledemo2", {revert: true, snap: [40, 40]});
});
 Draggable demo.
Draggable demo.Default options.
 Draggable demo.
Draggable demo.{snap:[60, 60], revert:true}
Draggables
- a global helper for accessing/managing all Draggable objects on a page
- (not needed for this course)
- properties:
drags,observers - methods:
register,unregister,activate,deactivate,updateDrag,endDrag,keyPress,addObserver,removeObserver,notify
Droppables
Droppables.add(element or id,
{ options }
);
- specifies an element as being able to be dragged
- options:
accept,containment,hoverclass,overlap,greedy - event options:
onHover,onDrop- each callback accepts three parameters: the
Draggable, theDroppable, and the event - Shopping Cart demo
- each callback accepts three parameters: the
Drag/drop shopping demo
<img id="product1" src="images/shirt.png" alt="shirt" /> <img id="product2" src="images/cup.png" alt="cup" /> <div id="droptarget"></div>
document.observe("dom:loaded", function() {
new Draggable("product1");
new Draggable("product2");
Droppables.add("droptarget", {onDrop: productDrop});
});
function productDrop(drag, drop, event) {
alert("You dropped " + drag.id);
}


Sortable
Sortable.create(element or id of list,
{ options }
);
- specifies a list (
ul,ol) as being able to be dragged into any order - implemented internally using
Draggables andDroppables - options:
tag,only,overlap,constraint,containment,format,handle,hoverclass,ghosting,dropOnEmpty,scroll,scrollSensitivity,scrollSpeed,tree,treeTag - to make a list un-sortable again, call
Sortable.destroyon it
Sortable demo
<ol id="simpsons"> <li id="simpsons_0">Homer</li> <li id="simpsons_1">Marge</li> <li id="simpsons_2">Bart</li> <li id="simpsons_3">Lisa</li> <li id="simpsons_4">Maggie</li> </ol>
document.observe("dom:loaded", function() {
Sortable.create("simpsons");
});
- Homer
- Marge
- Bart
- Lisa
- Maggie
Sortable list events
| event | description |
|---|---|
onChange
|
when any list item hovers over a new position while dragging |
onUpdate
|
when a list item is dropped into a new position (more useful) |
document.observe("dom:loaded", function() {
Sortable.create("simpsons", {
onUpdate: listUpdate
});
});
onChangehandler function receives the dragging element as its parameteronUpdatehandler function receives the list as its parameter
Sortable list events example
document.observe("dom:loaded", function() {
Sortable.create("simpsons", {
onUpdate: listUpdate
});
});
function listUpdate(list) {
// can do anything I want here; effects, an Ajax request, etc.
list.shake();
}
- Homer
- Marge
- Bart
- Lisa
- Maggie
Subtleties of Sortable events
- for
onUpdateto work, eachlimust have anidof the formlistID_index<ol id="simpsons"> <li id="simpsons_0">Homer</li> <li id="simpsons_1">Marge</li> <li id="simpsons_2">Bart</li> <li id="simpsons_3">Lisa</li> <li id="simpsons_4">Maggie</li> </ol>
- if the elements of the list change after you make it sortable (if you add or remove an item using the DOM, etc.), the new items can't be sorted
- must call
Sortable.createon the list again to fix it
- must call
Auto-completing text fields
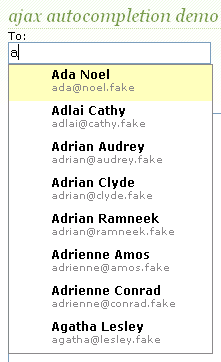
Scriptaculous offers ways to make a text box that auto-completes based on prefix strings:
-
Autocompleter.Local: auto-completes from an array of choices -
Ajax.Autocompleter: fetches and displays list of choices using Ajax
Using Autocompleter.Local
new Autocompleter.Local(
element or id of text box,
element or id of div to show completions,
array of choices,
{ options }
);
- you must create an (initially empty)
divto store the auto-completion matches- it will be inserted as a
ulthat you can style with CSS - the user can select items by pressing Up/Down arrows; selected item is given a
classofselected
- it will be inserted as a
- pass the choices as an array of strings
- pass any extra options as a fourth parameter between
{}- options:
choices,partialSearch,fullSearch,partialChars,ignoreCase
- options:
Autocompleter.Local demo
<input id="bands70s" size="40" type="text" /> <div id="bandlistarea"></div>
document.observe("dom:loaded", function() {
new Autocompleter.Local(
"bands70s",
"bandlistarea",
["ABBA", "AC/DC", "Aerosmith", "America", "Bay City Rollers", ...],
{}
);
});
Autocompleter styling
<input id="bands70s" size="40" type="text" /> <div id="bandlistarea"></div>
#bandlistarea {
border: 2px solid gray;
}
/* 'selected' class is given to the autocomplete item currently chosen */
#bandlistarea .selected {
background-color: pink;
}
Using Ajax.Autocompleter
new Ajax.Autocompleter(
element or id of text box,
element or id of div to show completions,
url,
{ options }
);
- when you have too many choices to hold them all in an array, you can instead fetch subsets of choices from the server using Ajax
- instead of passing choices as an array, pass a URL from which to fetch them
- the choices are sent back from the server as an HTML
ulwithlielements in it
- the choices are sent back from the server as an HTML
- options:
paramName,tokens,frequency,minChars,indicator,updateElement,afterUpdateElement,callback,parameters
Ajax.InPlaceEditor
new Ajax.InPlaceEditor(element or id,
url,
{ options }
);
- options:
okButton,okText,cancelLink,cancelText,savingText,clickToEditText,formId,externalControl,rows,onComplete,onFailure,cols,size,highlightcolor,highlightendcolor,formClassName,hoverClassName,loadTextURL,loadingText,callback,submitOnBlur,ajaxOptions - event options:
onEnterHover,onLeaveHover,onEnterEditMode,onLeaveEditMode
Ajax.InPlaceCollectionEditor
new Ajax.InPlaceCollectionEditor(element or id,
url,
{
collection: array of choices,
options
}
);
- a variation of
Ajax.InPlaceEditorthat gives a collection of choices - requires
collectionoption whose value is an array of strings to choose from - all other options are the same as
Ajax.InPlaceEditor
Playing sounds (API)
| method | description |
|---|---|
Sound.play("url");
|
plays a sound/music file |
Sound.disable();
|
stops future sounds from playing (doesn't mute any sound in progress) |
Sound.enable();
|
re-enables sounds to be playable after a call to Sound.disable()
|
Sound.play("music/java_rap.mp3");
Sound.play("music/wazzaaaaaap.wav");
-
to silence a sound playing in progress, use
Sound.play('', {replace: true}); - cannot play sounds from a local computer (must be uploaded to a web site)
Other neat features
-
slider control:
new Control.Slider("id of knob", "id of track", {options}); -
Builder- convenience class to replacedocument.createElement:var img = Builder.node("img", { src: "images/lolcat.jpg", width: 100, height: 100, alt: "I can haz Scriptaculous?" }); $("main").appendChild(img); - Tabbed UIs
11.1: Event-Handling
-
11.1: Event-Handling
- 11.1.1 The Event Object
- 11.1.2 Mouse Events
- 11.1.3 Keyboard and Text Events
- 11.1.4 Form Events
- 11.1.5 Page Events
- 11.1.6 Timer Events
-
11.2: Case Study: Multiplication Quiz
- very instructive example
- easy to understand (I hope!)
- you should read it
- ask questions in next class meetingif there is anyhing that you don't understand
JavaScript events
abort
|
blur
|
change
|
click
|
dblclick
|
error
|
focus
|
keydown
|
keypress
|
keyup
|
load
|
mousedown
|
mousemove
|
mouseout
|
mouseover
|
mouseup
|
reset
|
resize
|
select
|
submit
|
unload
|
-
the
clickevent (onclick) is just one of many events that can be handled -
problem: events are tricky and have incompatibilities across browsers
- reasons: fuzzy W3C event specs; IE disobeying web standards; etc.
- solution: Prototype includes many event-related features and fixes
Attaching event handlers the Prototype way
element.onevent = function; element.observe("event", function);
// call the playNewGame function when the Play button is clicked
$("play").observe("click", playNewGame);
-
to use Prototype's event features, you must attach the handler using the DOM element object's
observemethod (added by Prototype) - pass the event name as a string, and the function name to call
- handlers must be attached this way for Prototype's event features to work
-
observesubstitutes foraddEventListener(not supported by IE)
The event object
function name(event) {
// an event handler function ...
}
- Event handlers can accept an optional parameter to represent the event that is occurring. Event objects have the following properties / methods:
| method / property name | description |
|---|---|
type
|
what kind of event, such as "click" or "mousedown"
|
element() *
|
the element on which the event occurred |
stop() **
|
cancels an event |
stopObserving()
|
removes an event handler |
-
* replaces non-standard
srcElementandwhichproperties -
** replaces non-standard
return false;,stopPropagation, etc.
Mouse events
click
|
user presses/releases mouse button on the element |
dblclick
|
user presses/releases mouse button twice on the element |
mousedown
|
user presses down mouse button on the element |
mouseup
|
user releases mouse button on the element |
mouseover
|
mouse cursor enters the element's box |
mouseout
|
mouse cursor exits the element's box |
mousemove
|
mouse cursor moves around within the element's box |
Mouse event objects
The event passed to a mouse handler has these properties:
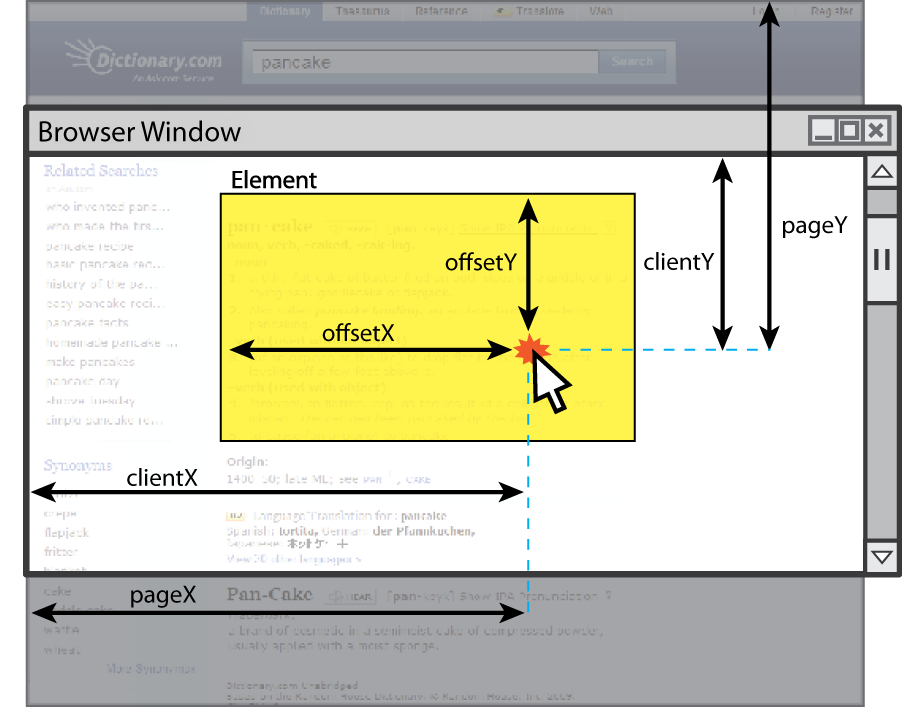
| property/method | description |
|---|---|
clientX, clientY
|
coordinates in browser window |
screenX, screenY
|
coordinates in screen |
offsetX, offsetY
|
coordinates in element (non-standard) |
pointerX(), pointerY() *
|
coordinates in entire web page |
isLeftClick() **
|
true if left button was pressed
|
-
* replaces non-standard properties
pageXandpageY -
** replaces non-standard properties
buttonandwhich
Mouse event example
<pre id="target">Move the mouse over me!</pre>
window.onload = function() {
$("target").observe("mousemove", showCoords);
};
function showCoords(event) {
$("target").innerHTML =
"pointer: (" + event.pointerX() + ", " + event.pointerY() + ")\n"
+ "screen : (" + event.screenX + ", " + event.screenY + ")\n"
+ "client : (" + event.clientX + ", " + event.clientY + ")";
}
Move the mouse over me!
Recap: The keyword this
this.fieldName // access field this.fieldName = value; // modify field this.methodName(parameters); // call method
- all JavaScript code actually runs inside of an object
-
by default, code runs in the global
windowobject (sothis===window)-
all global variables and functions you declare become part of
window
-
all global variables and functions you declare become part of
-
the
thiskeyword refers to the current object
Recap: Event handler binding
window.onload = function() {
$("textbox").observe("mouseout", booyah); // bound to text box here
$("submit").observe("click", booyah); // bound to submit button here
};
function booyah() { // booyah knows what object it was called on
this.value = "booyah";
}
- event handlers attached unobtrusively are bound to the element
- inside the handler, that element becomes
this(rather than thewindow)
Fixing redundant code with this
<fieldset> <label><input type="radio" name="ducks" value="Huey" /> Huey</label> <label><input type="radio" name="ducks" value="Dewey" /> Dewey</label> <label><input type="radio" name="ducks" value="Louie" /> Louie</label> </fieldset>
function processDucks() {
if ($("huey").checked) {
alert("Huey is checked!");
} else if ($("dewey").checked) {
alert("Dewey is checked!");
} else {
alert("Louie is checked!");
}
alert(this.value + " is checked!");
}
- if the same function is assigned to multiple elements, each gets its own bound copy
Page/window events
| name | description |
|---|---|
load,
unload
|
the browser loads/exits the page |
resize
|
the browser window is resized |
error
|
an error occurs when loading a document or an image |
contextmenu
|
the user right-clicks to pop up a context menu |
-
The above can be handled on the
windowobject. An alternative towindow.onload:
window.onload = function() { ... };document.observe("dom:loaded", function() { // attach event handlers, etc. });
Keyboard/text events
| name | description |
|---|---|
keydown
|
user presses a key while this element has keyboard focus |
keyup
|
user releases a key while this element has keyboard focus |
keypress
|
user presses and releases a key while this element has keyboard focus |
focus
|
this element gains keyboard focus |
blur
|
this element loses keyboard focus |
select
|
this element's text is selected or deselected) |
- focus: the attention of the user's keyboard (given to one element at a time)
Key event objects
| property name | description |
|---|---|
keyCode
|
ASCII integer value of key that was pressed (convert to char with String.fromCharCode)
|
altKey, ctrlKey, shiftKey
|
true if Alt/Ctrl/Shift key is being held
|
Event.KEY_BACKSPACE
|
Event.KEY_DELETE
|
Event.KEY_DOWN
|
Event.KEY_END
|
Event.KEY_ESC
|
Event.KEY_HOME
|
Event.KEY_LEFT
|
Event.KEY_PAGEDOWN
|
Event.KEY_PAGEUP
|
Event.KEY_RETURN
|
Event.KEY_RIGHT
|
Event.KEY_TAB
|
Event.KEY_UP
|
-
issue: if the event you attach your listener to doesn't have the focus, you won't hear the event
- possible solution: attach key listener to entire page body, outer element, etc.
Form events
| event name | description |
|---|---|
submit
|
form is being submitted |
reset
|
form is being reset |
change
|
the text or state of a form control has changed |
- Prototype adds the following methods to form controls' DOM objects:
activate |
clear |
disable |
enable |
focus |
getValue |
present |
select |
Prototype form shortcuts
$F("formID")["name"]
- gets parameter with given name from form with given id
$F("controlID")
-
$Ffunction returns the value of a form control with the given idif ($F("username").length < 4) { $("username").clear(); $("login").disable(); }
Stopping an event
<form id="exampleform" action="http://foo.com/foo.php">...</form>
window.onload = function() {
$("exampleform").observe("submit", checkData);
};
function checkData(event) {
if ($F("city") == "" || $F("state").length != 2) {
alert("Error, invalid city/state."); // show error message
event.stop();
return false;
}
}
- to abort a form submit or other event, call Prototype's
stopmethod on the event
Event-handling example
Use events to do some cool animations!
We use timer events, with methods setInterval and clearInterval
setInterval(code,millisec) returns ID of timer event
clearInterval(id_of_setinterval)

