CSSE 290 Web Programming
Lecture 9: PHP Objects, Form Basics
Reading: 6.1 - 6.2, 6.4
Except where otherwise noted, the contents of this document are Copyright 2012 Marty Stepp, Jessica Miller, and Victoria Kirst. All rights reserved. Any redistribution, reproduction, transmission, or storage of part or all of the contents in any form is prohibited without the author's expressed written permission.
Otherwise note: Claude Anderson was given permission to modify the slides for CSSE 290 at Rose-Hulman by author Jessica Miller. The authors' original slides, based on Web Programming Step by Step, can be seen at http://webstepbook.com.
Some of the examples in some days' slides are from David Fisher at Rose-Hulman, who was kind enough to allow me to use them. My intention is to mark these examples with [DSF].
PHP Objects
- 5.4: Advanced PHP (Objects)
- 6.1: Form Basics
- 6.2: Form Controls
- 6.3: Submitting Data
- 6.4: Processing Form Data in PHP
Why use classes and objects?
- PHP is primarily a procedural language
- small programs are easily written without adding any classes or objects
- larger programs, become cluttered with many disorganized functions
- grouping related data and behavior into objects helps manage size and complexity
Constructing and using objects
# construct an object $name = new ClassName(parameters); # access an object's field (if the field is public) $name->fieldName # call an object's method $name->methodName(parameters);
$zip = new ZipArchive();
$zip->open("moviefiles.zip");
$zip->extractTo("images/");
$zip->close();
- the above code unzips a file
- test whether a class is installed with the
class_existsfunction
Example of object use: Fetch file from web
# create an HTTP request to fetch student.php $req = new HttpRequest("student.php", HttpRequest::METH_GET); $params = array("first_name" => $fname, "last_name" => $lname); $req->addPostFields($params); # send request and examine result $req->send(); $http_result_code = $req->getResponseCode(); # 200 means OK print "$http_result_code\n"; print $req->getResponseBody();
- PHP's
HttpRequestobject can fetch a document from the web
Class declaration syntax
class ClassName {
# fields - data inside each object
public $name; # public field
private $name; # private field
# constructor - initializes each object's state
public function __construct(parameters) {
statement(s);
}
# method - behavior of each object
public function name(parameters) {
statements;
}
}
- Note that the name of the constructor begins with em>two underscores
- Inside a constructor or method, refer to the current object as
$this
Class example
<?php
class Point {
public $x;
public $y;
# equivalent of a Java constructor
public function __construct($x, $y) {
$this->x = $x;
$this->y = $y;
}
public function distance($p) {
$dx = $this->x - $p->x;
$dy = $this->y - $p->y;
return sqrt($dx * $dx + $dy * $dy);
}
# equivalent of Java's toString method
public function __toString() {
return "(" . $this->x . ", " . $this->y . ")";
}
}
?>
Class usage example
<?php # this code could go into a file named use_point.php include("Point.php"); $p1 = new Point(0, 0); $p2 = new Point(4, 3); print "Distance between $p1 and $p2 is " . $p1->distance($p2) . "\n\n"; var_dump($p2); # var_dump prints detailed state of an object ?>
Distance between (0, 0) and (4, 3) is 5 object(Point)[2] public 'x' => int 4 public 'y' => int 3
-
$p1and$p2are references toPointobjects
Basic inheritance
class ClassName extends ClassName {
...
}
class Point3D extends Point {
public $z;
public function __construct($x, $y, $z) {
parent::__construct($x, $y);
$this->z = $z;
}
...
}
- the given class will inherit all data and behavior from ClassName
Static methods, fields, and constants
static $name = value; # declaring a static field const $name = value; # declaring a static constant
# declaring a static method
public static function name(parameters) {
statements;
}
ClassName::methodName(parameters); # calling a static method (outside class) self::methodName(parameters); # calling a static method (within class)
- static fields/methods are shared throughout a class rather than replicated in every object
Abstract classes and interfaces
interface InterfaceName {
public function name(parameters);
public function name(parameters);
...
}
class ClassName implements InterfaceName { ...
abstract class ClassName {
abstract public function name(parameters);
...
}
-
interfaces are supertypes that specify method headers without implementations
- cannot be instantiated; cannot contain function bodies or fields
- enables polymorphism between subtypes without sharing implementation code
-
abstract classes are like interfaces, but you can specify fields, constructors, methods
- also cannot be instantiated; enables polymorphism with sharing of implementation code
Form Basics
- 5.4: Advanced PHP (Objects)
- 6.1: Form Basics
- 6.2: Form Controls
- 6.3: Submitting Data
- 6.4: Processing Form Data in PHP
Web data
- most interesting web pages revolve around data
- examples: Google, IMDB, Digg, Facebook, YouTube, Rotten Tomatoes
- can take many formats: text, HTML, XML, multimedia
- many of sites allow us to access their data
- some even allow us to submit our own new data
- most server-side web programs accept parameters that guide their execution
Recap: Query strings and parameters
URL?name=value&name=value...
http://www.google.com/search?q=deficit http://example.com/student_login.php?username=gandalf&id=1234567
- query string: a set of parameters passed from a browser to a web server
- often passed by placing name/value pairs at the end of a URL
- above, parameter
usernamehas valuegandalf, andsidhas value1234567 - parameters sent inquery string are known as GET parameters
- PHP code on the server can examine and utilize the value of parameters
- a way for PHP code to produce different output based on values passed by the user
Query parameters:
$_GET,
$_POST
$user_name = $_GET["username"];
$id_number = (int) $_GET["id"];
$eats_meat = FALSE;
if (isset($_GET["meat"])) {
$eats_meat = TRUE;
}
-
$_GET["parameter name"]or$_POST["parameter name"]returns a GET/POST parameter's value as a string - parameters specified as
http://....?name=value&name=valueare GET parameters - test whether a given parameter was passed with
isset
HTML forms
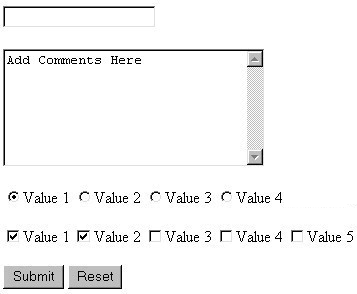
- form: a group of UI controls that accepts information from the user and sends the information to a web server
- the information is sent to the server as a query string
- JavaScript can be used to create interactive controls (seen later)
HTML form:
<form>
<form action="destination URL"> form controls </form>
- required
actionattribute gives the URL of the page that will process this form's data -
when form has been filled out and submitted, its data will be sent to the
action's URL - one page may contain many forms if so desired
Form example
<form action="http://www.google.com/search"> <div> Let's search Google: <input name="q" /> <input type="submit" /> </div> </form>
- must wrap the form's controls in a block element such as
div - let's try it ourselves!
6.2: Form Controls
- 6.1: Form Basics
- 6.2: Form Controls
- 6.3: Submitting Data
- 6.4: Processing Form Data in PHP
Form controls: <input>
<!-- 'q' happens to be the name of Google's required parameter -->
<input type="text" name="q" value="Rose-Hulman" />
<input type="submit" value="Go fish!" />
inputelement is used to create many UI controls- an inline element that MUST be self-closed
nameattribute specifies name of query parameter to pass to servertypecan bebutton,checkbox,file,hidden,password,radio,reset,submit,text, ...valueattribute specifies control's initial text
Text fields:
<input>
<input type="text" size="10" maxlength="8" /> NetID <br /> <input type="password" size="16" /> Password <input type="submit" value="Log In" />
Text boxes:
<textarea>
a multi-line text input area (inline)
<textarea rows="4" cols="20"> Type your comments here. </textarea>
- initial text is placed inside
textareatag (optional) - required
rowsandcolsattributes specify height/width in characters - optional
readonlyattribute means text cannot be modified
Checkboxes:
<input>
yes/no choices that can be checked and unchecked (inline)
<input type="checkbox" name="lettuce" /> Lettuce <input type="checkbox" name="tomato" checked="checked" /> Tomato <input type="checkbox" name="pickles" checked="checked" /> Pickles
- none, 1, or many checkboxes can be checked at same time
- when sent to server, any checked boxes will be sent with value
on:-
http://webster.cs.washington.edu/params.php?tomato=on&pickles=on
-
- use
checked="checked"attribute in HTML to initially check the box
Radio buttons:
<input>
sets of mutually exclusive choices (inline)
<input type="radio" name="cc" value="visa" checked="checked" /> Visa <input type="radio" name="cc" value="mastercard" /> MasterCard <input type="radio" name="cc" value="amex" /> American Express
- grouped by
nameattribute (only one can be checked at a time) - must specify a
valuefor each one or else it will be sent as valueon
Text labels:
<label>
<label><input type="radio" name="cc" value="visa" checked="checked" /> Visa</label> <label><input type="radio" name="cc" value="mastercard" /> MasterCard</label> <label><input type="radio" name="cc" value="amex" /> American Express</label>
- associates nearby text with control, so you can click text to activate control
- can be used with checkboxes or radio buttons
labelelement can be targeted by CSS style rules
Drop-down list:
<select>,
<option>
menus of choices that collapse and expand (inline)
<select name="favoritebeatle"> <option>Paul</option> <option>George</option> <option selected="selected">Ringo</option> <option>John</option> </select>
optionelement represents each choiceselectoptional attributes:disabled,multiple,size- optional
selectedattribute sets which one is initially chosen
Using <select> for lists
<select name="favoritebeatle[]" size="5" multiple="multiple"> <option>John</option> <option>George</option> <option>Paul</option> <option>Pete*</option> <option>Stu*</option> <option selected="selected">Ringo</option> </select>
- optional
multipleattribute allows selecting multiple items with shift- or ctrl-click-
must declare parameter's name with
[]if you allow multiple selections
-
must declare parameter's name with
optiontags can be set to be initiallyselected
Option groups:
<optgroup>
<select name="favoritebeatle"> <optgroup label="long-term members"> <option>John</option> <option>George</option> <option>Paul</option> <option>Ringo</option> </optgroup> <optgroup label="Temporary members"> <option>Pete</option> <option>Stu</option> </optgroup> </select>
- What should we do if we don't like the bold appearance of the
optgroups?
Reset buttons
Name: <input type="text" name="name" /> <br /> Food: <input type="text" name="meal" value="pizza" /> <br /> <label>Meat? <input type="checkbox" name="meat" /></label> <br /> <input type="reset" /> <input type="submit" value="Order now!" />
- when clicked, returns all form controls to their initial values
- specify custom text on the button by setting its
valueattribute
Common UI control errors
-
I changed the form's HTML code ... but when I refresh, the page doesn't update!
- By default, when you refresh a page, it leaves the previous values in all form controls
- it does this in case you were filling out a long form and needed to refresh/return to it
- if you want it to clear out all UI controls' state and values, you must do a full refresh
- Firefox: Shift-Ctrl-R (Mac: Shift-Command-R)
- Chrome: Ctrl-F5
Hidden input parameters
<input type="text" name="username" /> Name <br /> <input type="text" name="sid" /> SID <br /> <input type="hidden" name="school" value="RHIT" /> <input type="hidden" name="year" value="2016" />
- an invisible parameter that is still passed to the server when form is submitted
- useful for passing on additional state that isn't modified by the user
Grouping input:
<fieldset>,
<legend>
groups of input fields with optional caption (block)
<fieldset> <legend>Credit cards:</legend> <input type="radio" name="cc" value="visa" checked="checked" /> Visa <input type="radio" name="cc" value="mastercard" /> MasterCard <input type="radio" name="cc" value="amex" /> American Express </fieldset> <input type="submit" />
fieldsetgroups related input fields, adds a border;legendsupplies a caption- Also provides a handle for CSS to address
Styling form controls
element[attribute="value"] { property : value; property : value; ... property : value; }
input[type="text"] {
background-color: yellow;
font-weight: bold;
}
- attribute selector: matches only elements that have a particular attribute value
- useful for controls because many share the same element (
input)
6.4: Processing Form Data in PHP
- 6.1: Form Basics
- 6.2: Form Controls
- 6.3: Submitting Data
- 6.4: Processing Form Data in PHP
Example: Exponents
$base = $_GET["base"]; $exp = $_GET["exponent"]; $result = pow($base, $exp); print "$base ^ $exp = $result";
http://example.com/exponent.php?base=3&exponent=4
Example: Print all parameters
<?php foreach ($_GET as $param => $value) { ?>
<p>Parameter <?= $param ?> has value <?= $value ?></p>
<?php } ?>
http://example.com/print_params.php?name=Marty+Stepp&sid=1234567
Parameter name has value Marty Stepp
Parameter sid has value 1234567
-
or call
print_rorvar_dumpon$_GETfor debugging
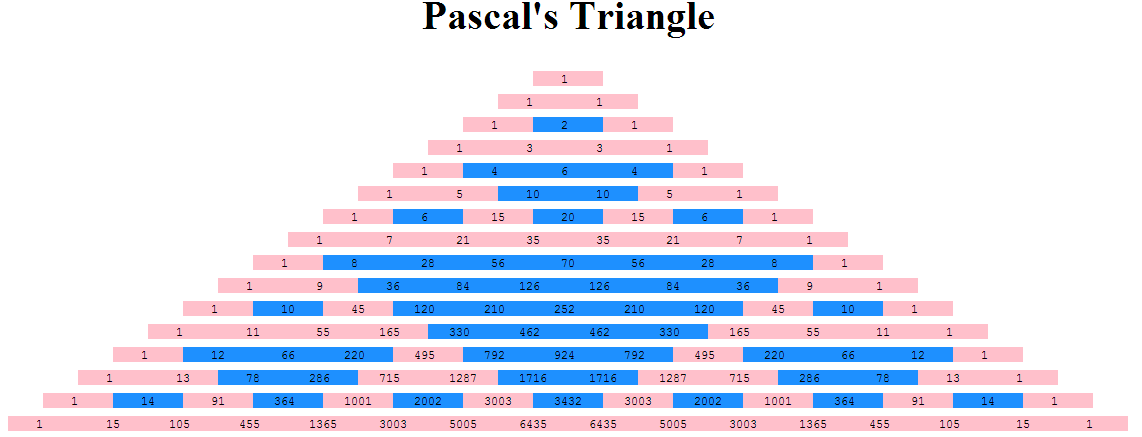
Exercise: form and resulting page
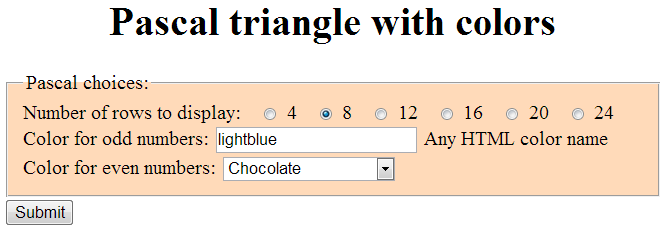
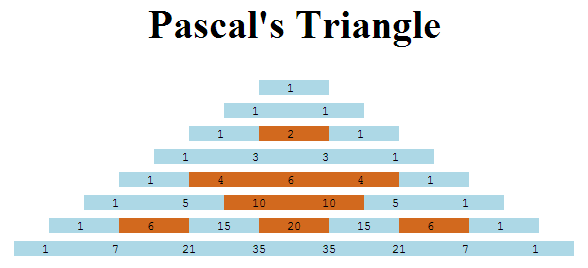
Exercise: more rows chosen
- Can you make it work for large number of rows? (it's okay if numbers are too small to see easily)
- Can you get rid of white space between rows? (I can't!)